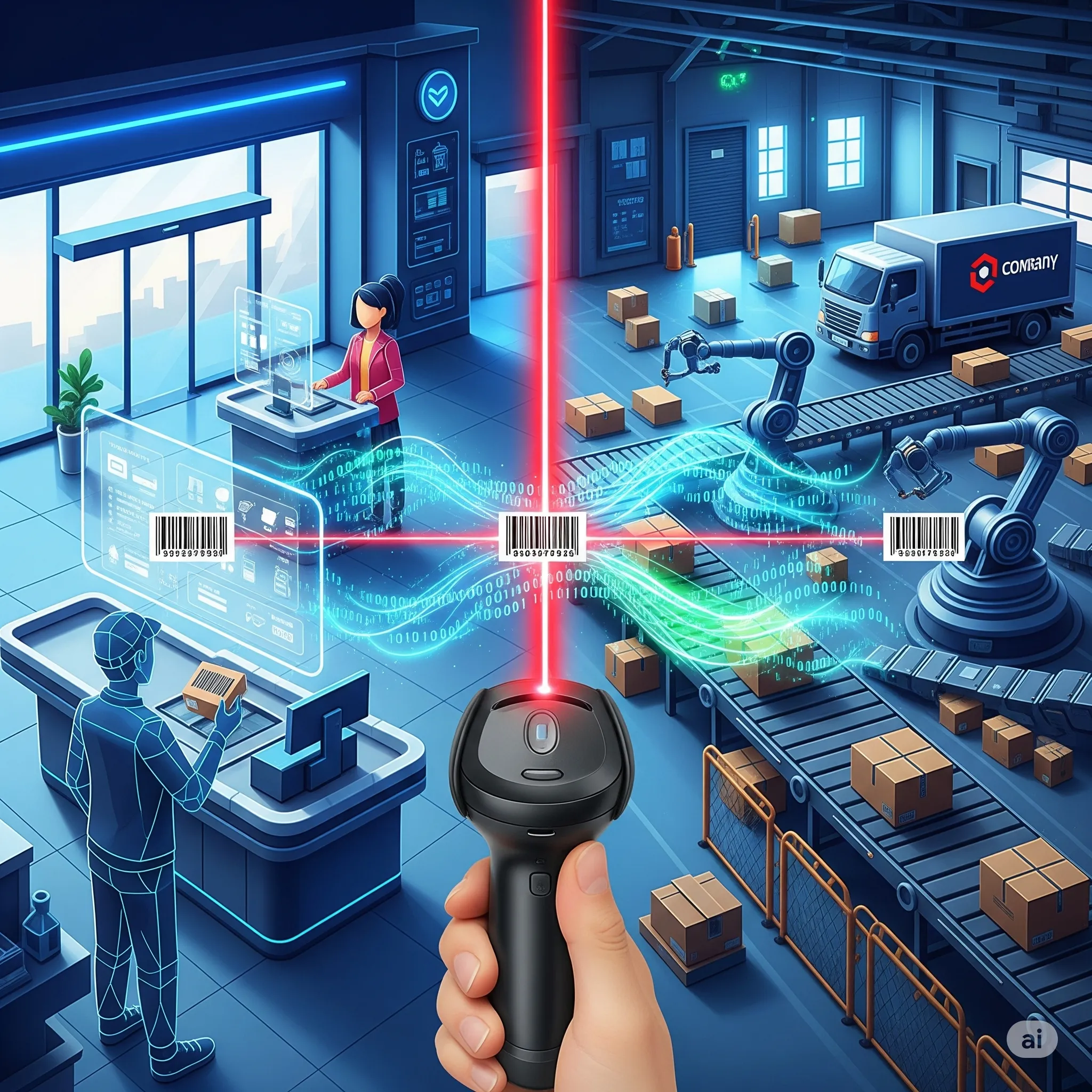
Barcode Scanners: Driving Retail and Logistics
Barcode Scanners: Driving Retail and Logistics
In the modern world, efficiency and accuracy are the two pillars of success for any business. While many technologies have contributed to this goal, few have had a more profound and widespread impact than the humble barcode scanner. These devices are not just for speeding up your grocery checkout; they are the silent workhorses that power two of the world's largest industries: retail and logistics. By replacing manual data entry with instant, error-free scanning, barcode scanners have become indispensable tools for managing inventory, streamlining supply chains, and delivering a better customer experience.
The Technology That Changed Everything
At its heart, a barcode scanner is an optical device that reads and decodes the information stored in a barcode—a machine-readable pattern of lines or squares. The scanner projects a beam of light onto the code, measures the reflected light, and then translates that pattern into a digital signal that a computer can understand. This simple, elegant process is the foundation for an incredible amount of efficiency.
For decades, the standard was the 1D (linear) barcode, like the UPC code you see on most products. Today, however, 2D barcodes like QR codes and Data Matrix codes are becoming increasingly common. These advanced codes can hold significantly more data, including URLs, images, and other information, and can be read by sophisticated imager scanners from any angle, even if they are damaged or smudged.
Barcode Scanners in Retail: The Checkout Revolution
The retail environment is where most of us have our first and most frequent encounters with barcode scanners. Their impact here is multi-faceted, extending far beyond simply scanning a price.
Streamlining the Point-of-Sale (POS)
The most obvious benefit of barcode scanners is how they accelerate the checkout process. Instead of a cashier manually typing in a product number, a quick scan retrieves the item's price and details from the system, reducing transaction time and minimizing human error. This speed not only benefits the retailer with faster turnover but also leads to a much better experience for the customer, who can get in and out of the store quickly.
Revolutionizing Inventory Management
Behind the scenes, the scanner is an invaluable inventory management tool. Every time a product is scanned at the checkout, the system automatically updates the inventory count. This provides retailers with a real-time, accurate picture of what's on their shelves and in their stockroom. This data is critical for:
-
Preventing Stockouts: Knowing exactly when to reorder an item ensures that popular products are always available.
-
Minimizing Overstock: Accurate data helps prevent buying too much product, which can lead to wasted capital and storage space.
-
Reducing Shrinkage: By accurately tracking items as they are sold, retailers can identify discrepancies and reduce losses from theft or administrative errors.
Driving Efficiency in Logistics and the Supply Chain
While retail relies on scanners to manage sales, the logistics industry depends on them for sheer survival. In the complex world of shipping, warehousing, and transportation, barcode scanners are the digital eyes and hands that ensure every package gets to the right place at the right time.
Warehouse Management and Order Fulfillment
In a modern warehouse, barcode scanners are a core component of the warehouse management system. When a shipment of goods arrives, each box is scanned, and the data is automatically logged into the system. As orders come in, warehouse workers use handheld scanners to locate, pick, and pack the correct items. This automated process minimizes errors and dramatically increases the speed of order fulfillment, which is a major competitive advantage in the age of e-commerce.
Tracking and Transparency
Barcode scanners provide unparalleled transparency in the supply chain. Each time a package is scanned—at the manufacturing plant, the distribution center, on the delivery truck, and at the customer's door—its location and status are instantly updated. This real-time data allows logistics companies to track millions of packages simultaneously, giving both businesses and customers peace of mind with accurate delivery estimates and tracking information.
Last-Mile Delivery
The "last mile" of a delivery—the final journey from the local distribution center to the customer's doorstep—is often the most complex. Barcode scanners are essential here, too. Delivery drivers use mobile scanners to confirm the correct package is loaded onto the truck and to capture a final scan at the point of delivery, serving as proof of receipt.
The Future of Barcode Technology
The barcode scanner market is projected to continue its strong growth, driven by the increasing demand for automation in retail and logistics. The future of this technology will likely be shaped by three key trends:
-
Advanced Imaging: The transition from laser to advanced 2D imagers is a major trend. These versatile scanners can read codes on any surface, including smartphone screens, which is essential for mobile coupons, digital tickets, and mobile wallets.
-
AI and Machine Learning: Future scanners will be more than just readers; they'll be smart devices. AI-powered scanners will be able to read damaged codes more accurately and provide richer, more predictive data about inventory and customer behavior.
-
Integration with IoT: Barcode scanners will become part of a larger network of connected devices (Internet of Things), providing seamless, automated data flow from the warehouse floor to the cloud, further streamlining supply chains.
Conclusion
In a world that demands speed, accuracy, and efficiency, barcode scanners have proven to be a cornerstone technology. From the retail checkout counter to the vast logistics networks that move our goods around the globe, they have quietly and effectively revolutionized how we do business. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the capabilities of these essential devices, ensuring that they remain at the heart of modern retail and logistics for years to come.
FAQs
Q1: What is the main difference between a 1D and a 2D barcode scanner? A1: A 1D scanner reads linear barcodes (like UPC codes) that only store data horizontally. A 2D imager can read both 1D and 2D barcodes (like QR codes), which store data both horizontally and vertically, allowing them to hold much more information in a smaller space.
Q2: How do barcode scanners improve efficiency in a warehouse? A2: Barcode scanners improve warehouse efficiency by enabling real-time inventory tracking, automating order fulfillment processes (picking and packing), and providing accurate data for shipping, which reduces errors and speeds up the entire supply chain.
Q3: Can a barcode scanner read a damaged barcode? A3: The ability to read a damaged barcode depends on the type of scanner. Modern 2D imagers are much more resilient than older laser scanners and are often capable of reading partially damaged, smudged, or torn barcodes.
Q4: Are barcode scanners secure? A4: Barcode scanners are data capture tools, not security devices. The security of the data they capture is handled by the connected software and database. The barcode itself is just an identifier that links to secure, centralized information.